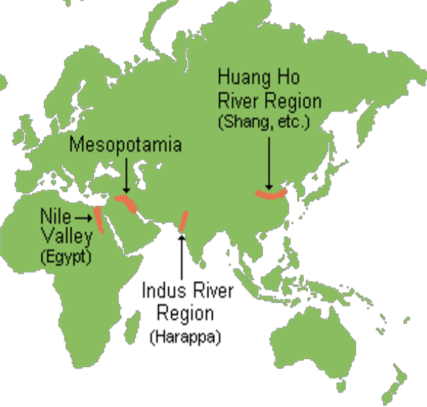
Mesopotamian (Sumerian) and Chinese civilization : General Knowledge USA Quiz.
By knowledgeterminal - December 14, 2018
Section one: USA map pointing (states and capital)
Section two: World map pointing (countries and capital)
Europe
Section three: USA historical events
1607
First successful English settlements were at Jamestown on May 13, 1607, by about 100 men and boys and women who came to Virginia from London, England.
Section four: world historical events
2560 BCE
Ancient Egyptians Build the Great Pyramid of Giza for Pharaoh Khufu
1754 BC
Babylonian King Hammurabi Issues the Code of Hammurabi, One of the Earliest Legal Codes
Section five: Mesopotamian (Sumerian) and Chinese civilization
Mesopotamia (land between rivers) situated
within the Tigris–Euphrates river system
Location: Western Asia (Iraq, Kuwait, parts of
Northern Saudi Arabia, the eastern parts of Syria, Southeastern Turkey)
In Mesopotamia world’s oldest major civilizations Sumerians,
Akkadians, Assyrians and Babylonians flourished
Rulers: Sumerians and Akkadians (later
Assyrians and Babylonians) majorly ruled Mesopotamia from 3100 BC to in 539 BC
when it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire (First Persian Empire (550–330
BC) founded by Cyrus the Great.) with the fall of Babylon. In 332 BC was
captured by Alexender the Great of Greek Seleucid Empire.
· Sumer was
the first urban civilization in ancient Mesopotamia
· Sumerian
city of Eridu (founded around 5400 BC) is regarded as the first city in the
world. It was on the coast of the Persian Gulf in Southern Mesopotamia
· Prehistoric
people known as Ubaidians are believed to be the first civilizing force in
Sumer
· Sargon of
Akkad ( Sargon the Great) founder of the Akkadian Empire conquered Sumer around
2270 BC.
· In
150 BC, Mesopotamia came under Parthian Empire.
· Western
parts of Mesopotamia coming under Roman control for short duration and in AD
226 the eastern regions came under Sassanid Persians.
· In 7th
century there were Muslim conquest of Persia of the Sasanian Empire and Muslim
conquest of the Levant from Byzantines
From around 10,000 BC. Mesopotamia became the location of the initial growth of the
Neolithic Revolution
Salient features:
· the
invention of the wheel
· the
planting of the first cereal crops
· development
of cursive script (wedge-shaped)
· The oldest
map was discovered in Babylonia around 2300 B.C.
From about 1754 BC (Middle Chronology), the Code of Hammurabi was Babylonian code of
law in ancient Mesopotamia. It
consists of 282 laws, advocating "an eye for an eye, a tooth for a tooth”
punishments
· Akkadian
Period is c. 2334 BC – c. 2154 or c. 2270 BC – c. 2083 BC
· Akkadian
Empire was the first ancient empire of Mesopotamia (centered in the city of
Akkad)
· The empire
united Akkadian and Sumerian speakers under one rule
· The
Akkadian Empire extended to the Levant, and Anatolia, Dilmun and Magan (modern
Bahrain and Oman)
· Akkadian
gradually replaced Sumerian as a spoken language
· After the
collapse of the Akkadian Empire (possibly due to drought) the people of
Mesopotamia eventually coalesced into two major Akkadian-speaking nations:
Assyria in the north and later Babylonia in the south as a small Amorite-ruled
state emerged in 1894 BC, which contained the minor administrative town of
Babylon
· During the
reign of Hammurabi and afterwards, Babylonia was called "the country of
Akkad"
· It was
often involved in rivalry with the older state of Assyria to the north and Elam
to the east in Ancient Iran. Babylonia briefly became the major power in the
region after Hammurabi 1810 BC – c. 1750 BC) was the sixth king of the First
Babylonian Dynasty, reigning from 1792 BC to 1750 BC
· The
Babylonian empire rapidly fell apart after the death of Hammurabi and reverted
to a small kingdom.
Babylonian state retained Sumerian language for religious
use and the written Akkadian language for official use, despite its Northwest
Semitic-speaking Amorite founders and Kassite successors, who spoke a language
isolate, not being native Mesopotamians
Chinese civilization Facts
- Civilizations originated along both the Yellow River (Huang Ho) (mainly) and Yangtze River.
- China was the first modern state having a centralized government
- The Chinese were also among the first people to write history. (e.g. Confucias’s Shujing, or Classic of History)
- Chinese History is conveniently divided into periods called Dynasties. The first Chinese dynasty was the Shang (the Xia dynasty was fictional)
- Shang reign overthrown by the Zhou (1046–256 BC). They introduced Mandate of to justify their reign. China didn’t even have an idea of “Heaven” and worshipped a “high god” called Shangdi. Using Mandate of Heaven, they explained that the Shang were able to conquer the Xia only because the Xia kings had lost the Mandate of Heaven
- The country crumbled into political chaos called the Warring States period, in which states warred over periods. During this period Confucius (551–479 BC), a minor official developed a philosophical and political system. He argued that by following the model of the sage emperors the Chinese emperor could bring order to China. If all men strive to be Junzi the “superior man” the society as a whole will run smoothly. This idea applies especially to the emperor, who is like the father to the whole country as he emphasized that the most important relation was the relation between father and son. He is also a traditional deity in Daoism.
- The period also saw Laozi/ Lao-Tze an ancient Chinese philosopher and writer. He wrote Tao Te Ching and was the founder of philosophical Taoism. Sun Tzu a Chinese general, military strategist, writer, and philosopher and the author of The Art of War was also from this period.
- This warring period ended when the Qin emperor (221 BC) was able to extend his power over most of the warring states. The Qin dynasty was one of the most important dynasties in Chinese history It re-unifed China under a single emperor for the first time in 500 years period and it gave the place its name, “Chin- uh.”
- Qin was replaced by the Han (206 BC–220 AD) a very important dynasty in China’s history. (period of stability and prosperity (golden age)) The name "Han" is used as the name of the Chinese people The country fell again into political chaos –there was no dynasty that ruled over all of China
- Country came under the Sui for short time, who were followed by the Tang.
- Most prosperous Chang'an (modern Xi'an). The capital was the largest city in the world at that time. The period saw Taizong, one of the greatest emperors in Chinese history and Xuanzang, a Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator who travelled to India. Chinese were the first in the world to use paper money, during the Tang Dynasty.
- Tang dynasty was replaced, after a short period of no dynasty
- Then came the Song, who saw a huge growth in China’s commerce that was still not enough to prevent them from being conquered by the Mongol Yuan in 1271, under the Great Khan of Mongol, Kublai Khan. This period saw the construction of grand canal and foundation of Beijing as the capital of the first foreign-led dynasty in China.
- As this dynasty became unpopular, there was a rise of the Ming (1368–1644), which was the dynasty that built the Great Wall
- They fell to the Manchus, who founded a dynasty that was called the Qing AD (1644–1912), which was the last dynasty
- In 1912 there was a Xinhai Revolution unsatisfied by the Qing's opposition to reform young officials inspired by the revolutionary ideas of Sun Yat-sen (the first provisional president of the Republic of China) overthrew Qing and created republic
·
Section six: quiz
QUESTIONS
1. What is the most common isotope of hydrogen?
2. What is the most abundant protein in the human body?
3. How much salt (NaCl) is in the average adult human body?
4. Who discovered Radium?
5. Who first discovered cells?
2. What is the most abundant protein in the human body?
3. How much salt (NaCl) is in the average adult human body?
4. Who discovered Radium?
5. Who first discovered cells?
ANSWERS
1. Protium
2. Collagen
3. 250 grams
4. Marie Curie.
5. Robert Hooke
2. Collagen
3. 250 grams
4. Marie Curie.
5. Robert Hooke